This version is out of date. Instead, use the new version UrsAI2PahoMqtt, which is based on the Eclipse Paho Java Client.
| Version | Adjustments |
|---|---|
| 1.0 (2019-10-31) | Initial Version |
| 1.1 (2019-11-09) | Wrong Packet-ID when publishing with QoS=1 |
| 1.2 (2019-12-04) | The user name was not forwarded. This inhibited the connection to a broker with authorisation. |
| 1.3 (2019-12-04) | Invalid authorization did not break the connection. |
| 1.4 (2019-12-05) | Wong computing of packet IDs > 127. |
| 1.5 (2020-01-24) | PINGREQUEST process corrected. |
| 1.6 (2020-01-30) | -PublishByteArray & PublishedByteArrayReceived
added. -KeepAlive was not accessible. |
| 1.7 (2020-03-06) | Possible null-pointer-exception in PublishByteArray is
prevented. Function IsNull added. |
| 1.8 (2020-03-20) | - Memory for unhandled messages is deleted on disconnect.
- When disconnecting the MessageHandler thread must stop before the TCP connection is terminated. - In the case of transmission errors (Xmit), LastErrorMessage contains the message type that caused the error. |
| 1.9 (2020-11-06) | Fixed incorrect string comparisons [String == "" -> String.isBlank()] |
Motivation
A small Raspberry Pi Zero serves as my MQTT broker in my WiFi. It would be nice if I could use the App Inventor von MIT to develop my own apps for my smartphone that could be used to communicate with this broker. While there are ready MQTT extensions for the App Inventor, they require additional JavaScript or external configuration files. The MQTT client component presented here works completely independently and does not require any external elements. It fully supports the MQTT protocol version 3.1.1 (Exception: Subscribe and Unsubscribe can only specify a single topic, not a list. Such lists can be handled poorly with the App Inventor.).
Content
Connecting to the Broker (Connect, Disconnect, ConnectionState, ConnectionStateChanged)
Subscribe to topics and receive messages (Subscribe, Unsubscribe, PublishedReceived)
Download
The ZIP archive UrsAI2Mqtt for download. The archive contains the source code, the compiled binary to upload to the App Inventor and a sample application.
Usage
The OASIS standard for the MQTT protocol can be found here: http://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v3.1.1/os/mqtt-v3.1.1-os.html. A detailed explanation of the MQTT basics is available at HiveMQ: MQTT Essentials.
Before the MQTT client can be connected to an MQTT broker, the connection options must first be set (see section Setting up the client). The connection to the broker is then created using the Connect method (section Connecting to the Broker). The ConnectionStateChanged event reports any change in the connection state. After work has been completed, the connection to the broker can be cleared using the Disconnect method.
With the different variants of the method Publish, messages are sent to the broker (section Send messages).
The Subscribe method can be used to determine to which topics the client wants to receive messages (Subscribe to Topic section). Subscription to the topics can be canceled using the Unsubscribe method. The receipt of a message about the subscribed topic is reported via the PublishedReceived event.
The component also provides error handling tools (section Error).
Explanations of how it works can be found in chapter MQTT: how it works (German, translated by google)
Setting up the client
Bevor eine Verbindung zu einem Broker hergestellt werden kann, müssen der Komponente die Verbindungsdaten mitgeteilt werden. Dies geschieht am einfachsten über das Eigenschaftenfenster des Designers.
To connect to a broker, the component needs to know the connection options. The easiest way to do this is via the properties window of the designer.
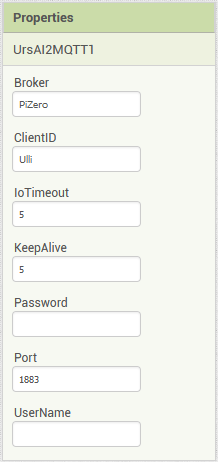 |
|
All connection options can also be set or retrieved via appropriate blocks:
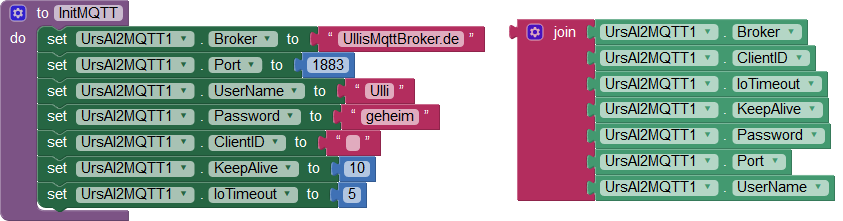
Connecting to the Broker (Connect, Disconnect, ConnectionState, ConnectionStateChanged)
The connection to the broker is made using the Connect method and terminated using the Disconnect method. External events can affect the connection to the broker too, e.g. loss of connection to the network. The current connection state can be retrieved via the ConnectionState property. If the state of the connection changes, the ConnectionStateChanged event is raised.
Methods for connection establishment and termination
The method Connect is available in two variants, without (Connect) and with "Last Will" (ConnectWithLastWill).
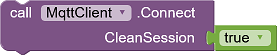 |
Establishes a connection without specifying a "last will". boolean CleanSession indicates whether to link to a previously aborted session. |
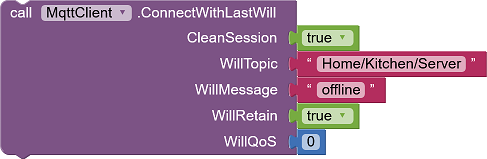 |
Establishes a connection with an indication of a "last will". boolean CleanSession indicates whether to link to a previously aborted session. WillTopic, WillQoS, WillRetain and WillMessage are the same as described in the Publish method (see Sending Messages). |
The planned termination of the connection is done via the method Disconnect. The method has no other parameters.
 |
Note: The information deposited with 'Last Will' only comes into effect if the connection was interrupted irregularly. If the connection is connected by Disconnect, the last will is discarded. Here, the client is responsible for sending appropriate messages before calling Disconnect. |
Connection states
The current connection status can be queried at any time via the ConnectionState property.
 |
int ConnectionState: see the following table. |
Possible states are:
| Code | State | Meaning | Allowed methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Disconnected | The client is not connected to a broker. | Connect |
| 1 | Connecting | The client tries to connect to the broker. | - |
| 2 | Connected | The client is connected to a broker. | Subscribe, Publish, Disconnect |
| 3 | Disconnecting | The client is disconnecting from the broker. | - |
| 4 | ConnectionAborted | The connection could not be established due to an error or was interrupted. Cause of error can be retrieved via the property LastErrorCode and LastErrorMessage. | Connect |
The following state diagram explains the process of connection establishment and termination:
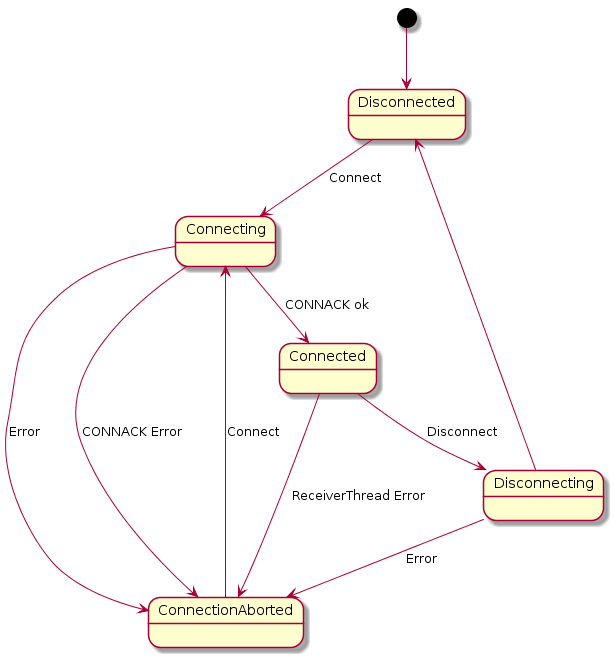
The MQTT client starts in the Disconnected (0) state. When the Connect method is called, it enters the state Connecting (1). An attempt is made to establish a TCP connection to the MQTT broker and to send a MQTT message of type CONNECT to the broker. If this does not succeed (Error) or if no message of the CONNACK type is received by the broker, the client enters the state ConnectionAborted (4).
When a message of type CONNACK is received, it is verified that the broker accepts the connection request from the client. If this is not the case (CONNACK Error), the network connection is terminated and the client enters the state ConnectionAborted (4). If the broker accepts the connection (CONNACK ok), the client enters the state Connected (2).
Disconnection begins when the Disconnect method is called. The client enters the state Diconnecting (3). First, a DISCONNECT message is sent to the broker. If this succeeds the client goes into the state Diconnected (0). In the event of an error (Error), the status changes to ConnectionAborted (4).
If an error occurs during operation (ReceiverTreadError), the network connection is disconnected and the status changes to ConnectionAborted (4).
Ereignis Verbindungszustand hat gewechselt
Ändert sich der Verbindungszustand, wird das Ereignis ConnectionStateChanged ausgelöst.
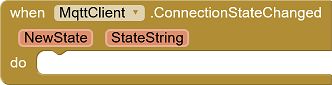 |
NewState: Numerischer Wert des Zustands (0..4, see
above) StateString: Bezeichnung des Zustands ("Disconnected", etc) |
Subscribe to topics and receive messages (Subscribe, Unsubscribe, PublishedReceived)
Subscribe to Topics
Subscribing to news topics is done through the method Subscribe.
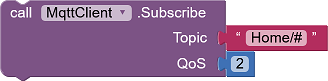 |
String Topic: Topic to subscribe. Wildcards are allowed. int QoS: Desired service level with which these messages are to be received. |
Through the SuBackReceived event, the broker reports which maximum QoS is supported for this topic. This is usually the requested level.
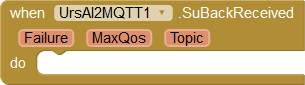 |
boolean Failure: The subscription was unsuccessful. int MaxQoS: Maximum QoS for this Topic. String Topic: Topic that has been subscribed. |
Unsubscribe
Unsubscribing is done using the method Unsubscribe.
 |
String Topic: Subscribtion to be canceled. Wildcards
are allowed. |
Receiving Messages
Received messages trigger the PublishedReceived event:
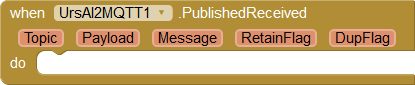 |
String Topic: Topic of this message. String Payload: Message content in binary format (see below) String Message: Message as String boolean RetainFlag: Indicates whether this is a retained message. boolean DupFlag: Indicates whether it is a repeated delivery. |
Message contents of MQTT messages are byte fields. These byte fields are provided as a string encoded via the Payload parameter. The coding procedure is described in the section Binary data. However, most of the messages is text in "UTF-8" format. Therefore, an attempt is made to convert the byte field to text. If this succeeds, the text is available under the parameter Message. Otherwise, Message contains an empty string.
Sending Messages (Publish)
There are three methods for sending messages.
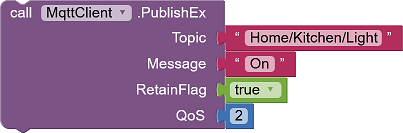 |
Default publishing method
Topic: Topic of this message. Message: Message as a string. RetainFlag: Indicates whether the message is a retained message. QoS: Service level for this publishing. |
|
 |
Simplified publishing Topic: Topic of this message. Message: Message as a string. RetainFlag is internally set to false. QoS is 0. |
|
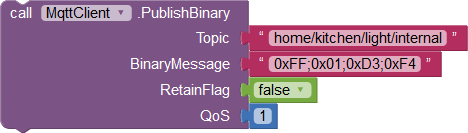 |
Publishing binary messages Topic: Topic of this message. BinaryMessage: Binary values encoded as a string. RetainFlag: Indicates whether the message is a retained message. QoS: Service level for this publishing. |
Binary data
App Inventor has no byte fields. Byte fields are rarely needed. In this component, binary data is encoded via a string. This is a string of encoded bytes separated by a comma (',') or semicolon (';').
Each bytes could be coded like “0xff” or “0xFF” or “0Xff” or “0XFF” or “#ff” or “#FF” for HEX input or “255” for decimal input or “0377” for octal input.
You can mix it if you want: “0xFF;255,#ff” is valid.
You can insert blanks before and after the number: “ 0xFF ; 255, #ff” is valid too.
A trailing comma or semicolon will be ignored: “0xFF;255,#ff” and “0xFF;255,#ff;” are identical
Upon receiving data, the received packet is translated into a semicolon separated string of decimal numbers, e.g. "123; 33; 0; 44". In the AI2 app you can use String.Split to get a list of bytes.
For the consversion I use this algorithm:
1) replace all commas by semicolons
2) split the
string by semicolons
3) delete leading and trailing blanks
4) convert to integer with
Integer.decode ()
5) check for values < 0 or > 255.
Binary data II - Byte-Array
For another project it was necessary to send and receive fields of type byte[] (byte array). App Inventor cannot handle byte arrays directly, but they can be exchanged as variables of the general type Object between extensions. For my WebCam project, JPEG images could be taken and sent via MQTT. The Android Camera API delivers the JPEG data as a byte array. The blocks PublishByteArray, SubscribeByteArray and PublishedByteArrayReceived are available for handling byte arrays.
PublishByteArray
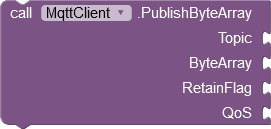
This block corresponds to the PublishEx method. Instead of the Message parameter there is the ByteArray parameter. Here the output of another extension is connected, which supplies a byte array. Standard blocks in the App Inventor are not able to create byte arrays.
SubscribeByteArray
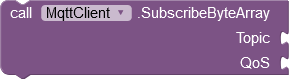
This block corresponds to the Subscribe method. All received messages that match the specified topic are interpreted as a byte array and forwarded to the PublishedByteArrayReceived event. Wildcards for the Topic parameter are allowed. When choosing topics and subscriptions, you have to be careful that the incoming messages are sorted correctly. The MQTT client checks in the order of byte array subscriptions whether a byte array has been subscribed under the transmitted topic. As soon as a hit is scored, PublishedByteArrayReceived is called. PublishedReceived is only triggered if no hit is scored here.
The comparison is based on the following algorithm https://github.com/iosphere/mosquitto, source: lib/util_mosq.c, method: mosquitto_topic_matches_sub.
PublishedByteArrayReceived
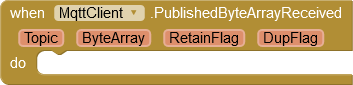
Dieses Ereignis wird ausgelöst, wenn über das Topic der empfangenen Nachricht (s. SubscribeByteArray) erkannt wird, dass ein Byte-Array empfangen wurde. Die Variable ByteArray kann an eine Extension weiter gegeben werden, die Byte-Arrays verarbeiten kann. Eine direkte Verwendung durch App Inventor Standard-Blöcke ist nicht möglich.
This event is triggered when the topic of the received message (see SubscribeByteArray) detects that a byte array has been received. The ByteArray variable can be passed to an extension that can process byte arrays. Direct use by App Inventor standard blocks is not possible.
IsNull
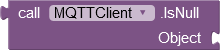
With this function you can test whether a pointer points to an object.
Error Handling
The following properties are available for handling error cases:
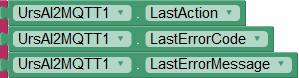 |
LastAction: Name of the last executed action, e.g. "Connect" LastErrorCode: error code of the last error (see below.) LastErrorMessage: textual description of the error, e.g. "Unacceptable protocol version" |
Wichtiger Hinweis: Die genannten Eigenschaften enthalten nur Hinweise auf wahrscheinliche Fehlerereignisse. Viele Aktionen werden asynchron ausgeführt. Da ist die Fehlerverfolgung nicht immer einwandfrei möglich.
Important note: The properties mentioned contain only indications of probable error events. Many actions are executed asynchronously. For these the error tracking is not always possible properly.
| Code | Bedeutung | Text | Anmerkung |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Connection was successfully established. | ||
| 1 | Connection refused, unacceptable protocol version. The Server does not support the level of the MQTT protocol requested by the client. | Unacceptable protocol version | Reported by the broker via CONNACK message. |
| 2 | Connection refused, identifier rejected. The Client identifier is correct UTF-8 but not allowed by the Server. | Identifier rejected | Reported by the broker via CONNACK message. |
| 3 | Connection refused, server unavailable. The Network Connection has been made but the MQTT
service is unavailable. |
Server unavailable | Reported by the broker via CONNACK message. |
| 4 | Connection refused, bad user name or password. The data in the user name or password is
malformed. |
Bad user name or password | Reported by the broker via CONNACK message. |
| 5 | Connection refused, not authorized. The Client is not authorized to connect. | Not authorized | Reported by the broker via CONNACK message. |
| -1 | Calling this method is not possible in the current operating state. | Invalid state | The current state must be Disconnected or ConnecteionAborted. IsDisconnected gets the right value. |
| -2 | The port parameter is outside the range of valid port values or the hostname parameter
is empty. |
Invalid Endpoint | Problem with assembling the IP endpoint (Java
InetSocketAddress) or Java Socket Fehler |
| -3 | A security manager is present and permission to resolve the host name is denied. |
Security violation | Problem with assembling the IP endpoint (Java InetSocketAddress) |
| -4 | Timeout expires before connecting. | Connection timeout | Java Socket Fehler |
| -5 | An error occurred during the connection. |
IO-Error | Internal error Java Socket Fehler |
| -6 | The socket streams could not be created. | Socket getStream problem | Internal error Java Socket Fehler |
| -7 | A blocking-mode-specific operation is invoked upon a channel in the incorrect blocking mode. | Illegal blocking mode | Formal internal error, should never appear. |
| -8 | Timeout during data reception. | Read timeout | Timeout when reading a received message. |
| -9 | The received message has an invalid format. | Invalid format | |
| -10 | Error sending a MQTT message. | Xmit failure | |
| -11 | The server did not respond to a ping request. | Ping failure | The connection to the server no longer exists. |
| -12 | Topic not specified or empty. | Empty topic | Specifying a topic is mandatory for some messages. |
| -13 | The message could not be converted to a byte field. | Invalid binary code | Details on coding: see section Binary data. |
Example
The example includes two apps that communicate with each other via MQTT. The first app, MQTTKitchenLight, emulates a simple lamp. A switch can be used to switch the lamp on and off.
This lamp connects to an MQTT broker and, when connected, publishes the current state (on, off, offline). In addition, the lamp can receive commands via MQTT (toggle) and respond accordingly.
The second app, MQTTKitchenLightControl, receives the status messages of the first app via MQTT and displays them. By clicking the switch button toggle commands are sent to the first app.
MQTTKitchenLightControl has a Screen named "Settings" with which you can set the connection data. With MQTTKitchenLight, there is no "Settings" screen implemented, the user name and password must be specified via the designer properties when creating the app. When entering the data you have to pay attention to the auto-completion of Android. It likes to insert additional characters, including spaces.
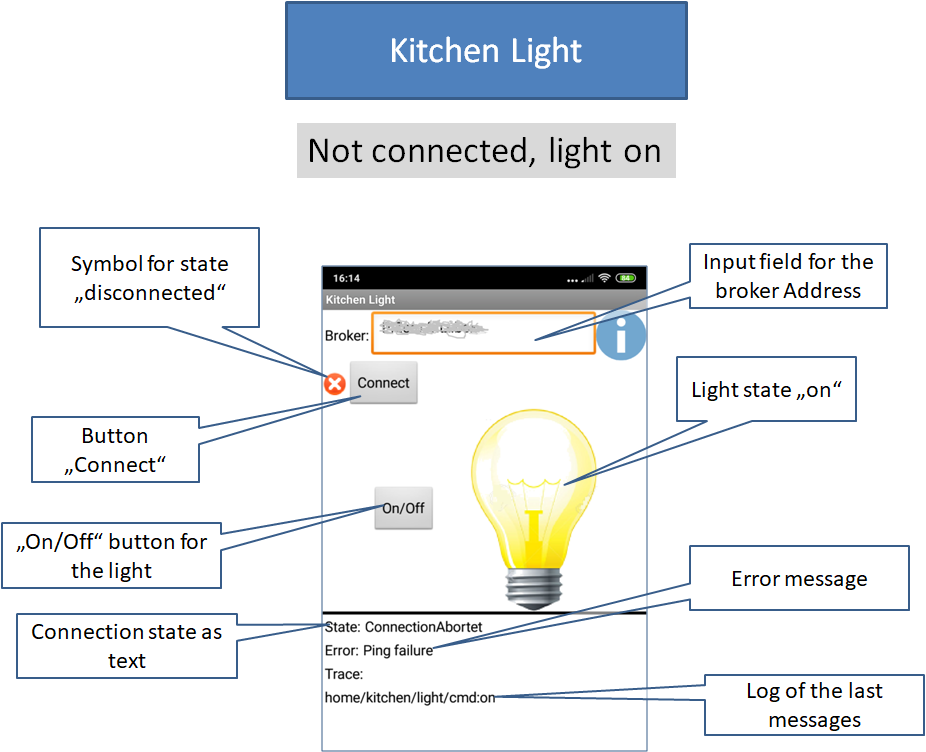
App MQTTKitchenLight
The following two pictures show screenshots of the app in two different states with explanation of the screen elements.
 |

|
Functionality
MQTTKitchenLight, the emulated lamp, starts with the lamp status off. If the "On / Off" button is pressed, the status changes to on and the next time it is pressed back again to off. The app sends its current status, "on" or "off", each time the lamp status changes with topic "home/kitchen/light/state" to the MQTT broker. The message is sent with a set retain flag, so that later added controllers immediately receive the current status when they log on to the broker.
The controller also needs to know if the app, i.e. the lamp, is online. Therefore, the app sends the message "offline" before disconnecting under the same topic. In order to ensure this even in the case of an unforeseen disconnection, a corresponding "Last Will" will be set up when connecting to the server
The app subscribes to the topic "home/kitchen/light/cmd". If it receives a message under this topic, the lamp is state is toggled. The message content should be "toggle", but this will not be evaluated.
App MQTTKitchenLightControl
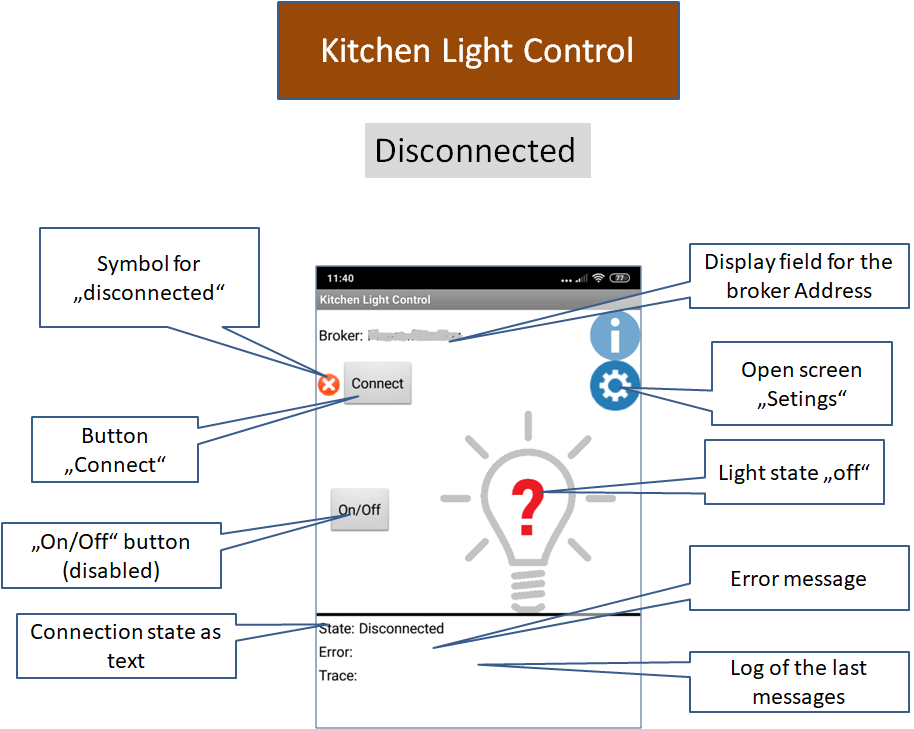 |
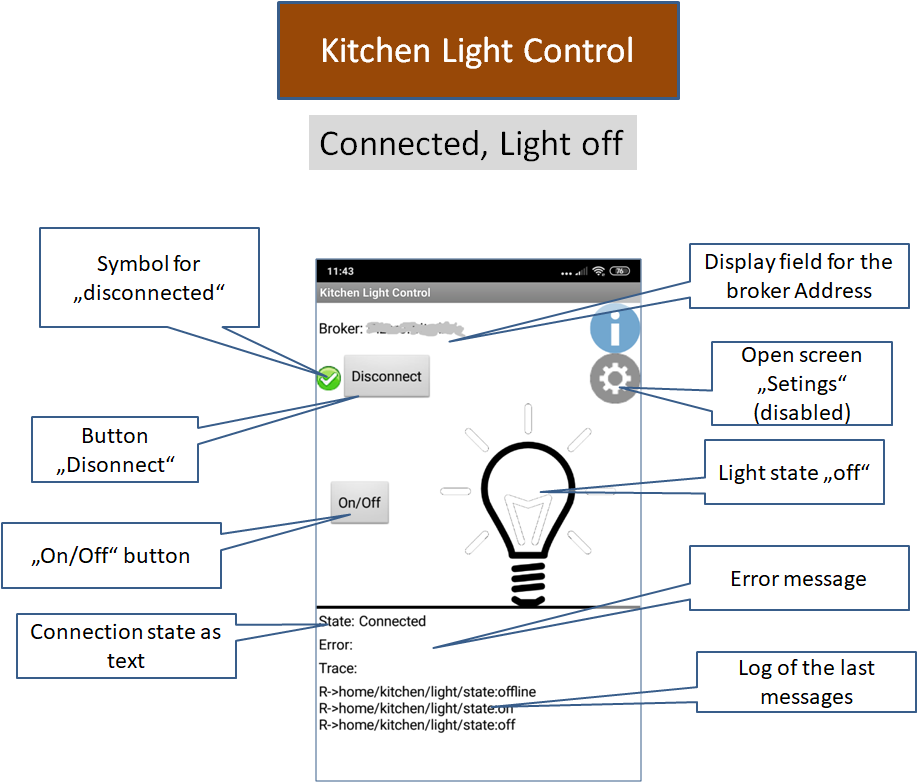
|
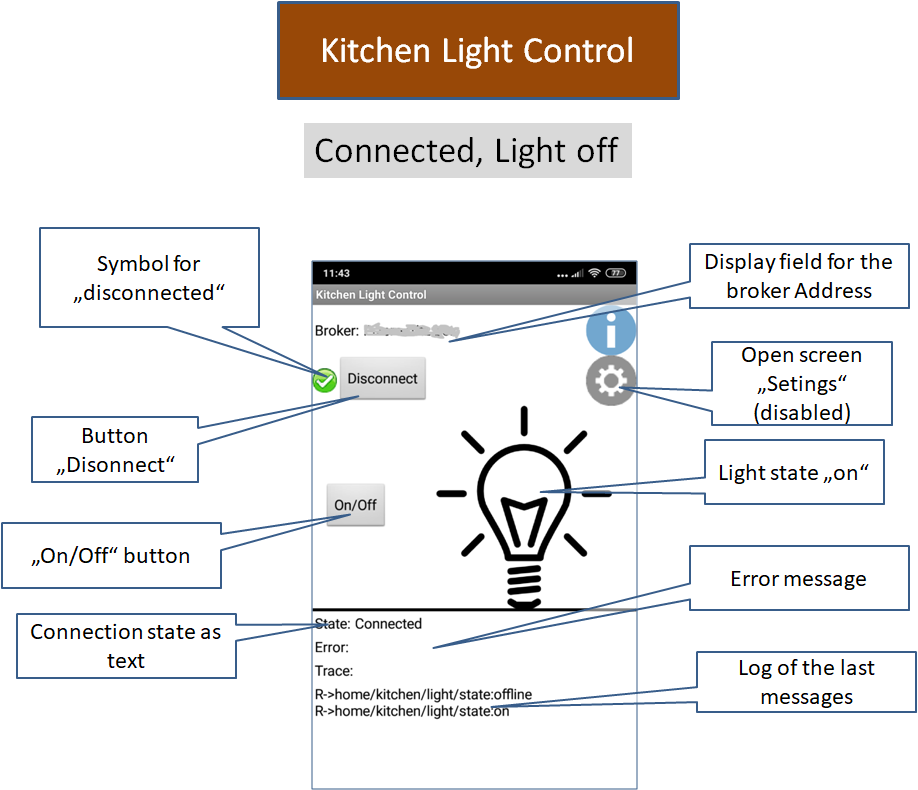
|
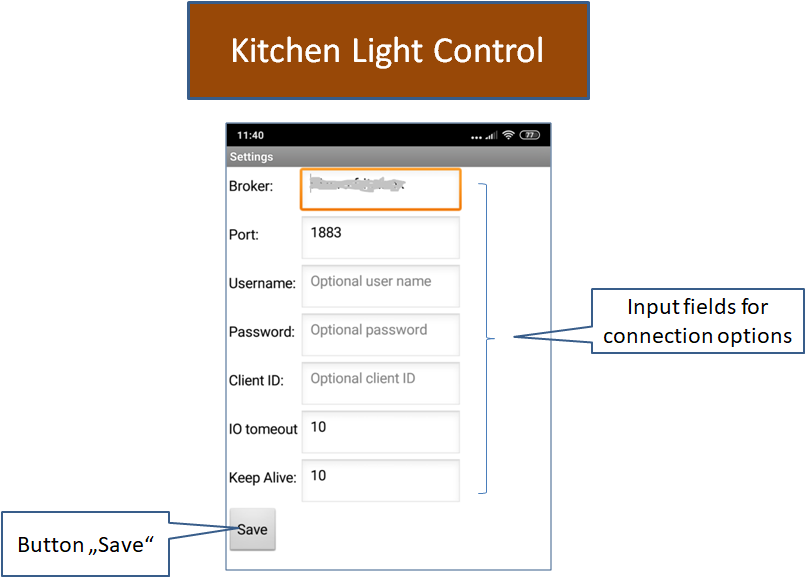
|
Functionality
The app has three states for the lamp: unknown (offline), on (on) and off (off). In the unconnected state, the state is basically unknown. After connecting with the broker, the app receives status information from the server (topic "home/kitchen/light/state"). The app MQTTKitchenLight publishes the current status of the lamp as a message with set retain flag, or the state offline, if the connection is disconnected or interrupted (Last Will). The app displays the lamp state accordingly.
In the connected state (app connected and current state on or off) the button "On/Off" is activated. If pressed, the app sends the message "toggle" to the broker with the topic "home/kitchen/light/cmd". If the MQTTKitchenLight app receives this message, it will toggle the lamp status and send a message with the new status.
The app has an additional dialog with which the connection options could be set.
The system can run any number of MQTTKitchenLightControl apps and control a single MQTTKitchenLight app. If you want to control several apps of type MQTTKitchenLight, you have to make the topics configurable.
Tools
For developing own extensions I gathered some tips: AI2 FAQ: Develop Extensions.