| Version | Modifications |
|---|---|
| 1.0 (2020-04-16) | Initial version |
| 2.0 (2020-04-29) | - Allows the evaluation of start and return values - Start as an independent or dependent process |
| 2.1 (2020-06-03) | MyAppName, MyPackageName added |
| 2.2 (2021-05-12 |
There were problems with devices from Android 10 and devices from Xiaomi (see notes). These properties added: CanDrawOverlays, CanLaunchFromBackground,CurrentLanguage, IsXiaomi, Manufacturer, PermissionDelay, VersionName, VersionSDK These methods: CheckBackgroundLaunchPermission, LaunchAppFromIntent, LaunchForResultFromIntent, OpenMiuiPermissionEditor Event AfterBackgroundPermssion added. Permissions added: SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW & ACTION_MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION The additional LauncherIntent block offers further options for how the app to be started should be executed. |
| 2.3 (2021-05-12) | Starting an AI2 app (intent type Screen) did not work with Kodular if the package name was changed. |
| 2.4 (2021-05-15) | Starting an AI2 app (intent type Screen) did not work with Kodular if the package name was changed. Further changes were necessary. |
| 2.5 (2021-05-13) | Property FlagNewTask at LauncherIntent
was ignored but is needed since Android 10. Default for property FlagNewTask is true. |
| 2.6 (2023-09-10) | As of Android 11, the QUERY_ALL_PACKAGES permission is necessary if you want all files to be listed in the getNameList or getPackageList function. |
Motivation
App Inventor enables other activities to be started with the ActivityStarter component. Unfortunately, starting installed apps is very cumbersome. According to the instructions, the .apk of the app to be started must be downloaded and the package name found. Both are neither easy nor always possible.
This extension simplifies starting apps.
Note for users of devices with Android 10 and up:
Since Android 10, an app needs additional permissions (SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW) if it wants to start another app while it is running itself in the background (see Restrictions on starting activities from the background, last point). This permission cannot be set by program, but has to be confirmed by the user via a dialog (see Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices). A possible solution to the problem is presented in the example.
Note for users of devices from the manufacturer Xiaomi:
With Xiaomi devices, regardless of the Android version installed, a additional permission is required if an app wants to start another app while it is itself running in the background. This permission cannot be not set by the program, but has to be confirmed by the user via a dialog (see Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices). The program cannot query whether this permission has already been granted. A possible solution to the problem is presented in the example.
Users of Xiaomi devices with Android 10 and newer must grant both permissions.
Content
Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices
Data exchange between two AI2 apps
Download
The ZIP archive UrsAI2AppLauncher for Download. The archive contains the source code, the compiled binary for uploading to App Inventor and a sample application.
Usage
Package Names
You must know the package name (e.g. "de.ullisroboterseite.ursai2applauncher") of an app to launch it. The method getNameList provides a list of the names of all apps that can be launched. There is a filter option to make a preselection. The list can, for example, be presented in a ListPicker component.
The PackageFromName method returns the package name associated with the specified app. The package name can then be used to start the designated app.
Launch modes
The app to be launched can be started in two ways:
- The app can be launched as an independent process, i.e. the starting and the launched app work completely independently of each other. The methods for this start with LaunchApp...
- The app can be started as a dependent process, i.e. the starting app pauses until the started app is ended. Here it is possible to return values from the launched app to the calling one. The methods for this option start with LaunchForResultApp...
In both cases, the started app can be launched with start values.
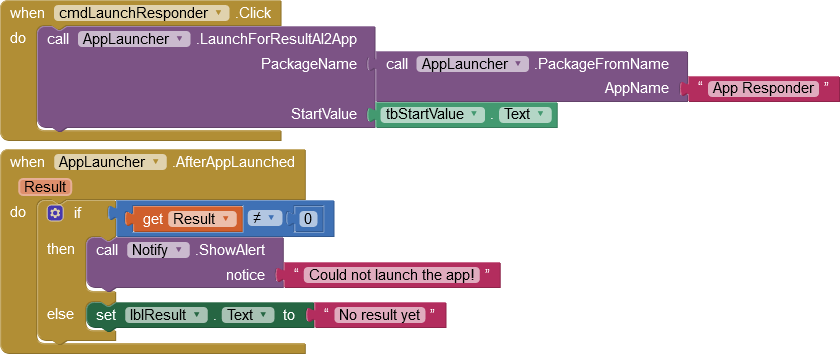
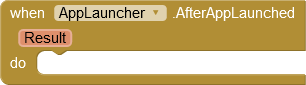
After starting an app, the AfterAppLaunched event is triggered. A parameter indicates whether the app was started successfully.
Start values
In Android an app is launched via an Intent. An intent is a abstract description of an operation to be performed. The intent contains all the information needed to start an app and also contains the data to be exchanged.
Data to be exchanged between apps can be stored in the intent as so-called Extras. Extras are a list of key-value pairs. The started app can retrieve and evaluate these values.
The app to be launched can be supplied with start values via different variants of the Launch... methods.
- First of all, the app can be started without any additional start value (LaunchApp, LaunchAppForResult).
- If the app to be lauched is an AI2 app, the AI2 standard method for parameter transfer can be used. AI2 evaluates the "APP_INVENTOR_START" key and provides the associated value via the Control - getStartValue or Control - getPlainStartText method. The parameter StartValue is stored with the key "APP_INVENTOR_START" through the methods LaunchAI2App, LaunchForResultAI2App.
- LauchAppExtra and LauchForResultAppExtra allow the transfer of a single key-value pair.
- LauchAppExtraList and LauchForResultAppExtraList transfer a list of key-value pairs.
Return Values
The following section is only relevant for apps started as a dependent process. Only these can return values.
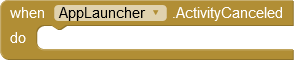
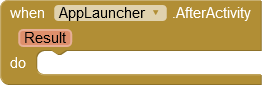
Always the called app can be canceled without returning results. In this case, the ActivityCanceled event is triggered.
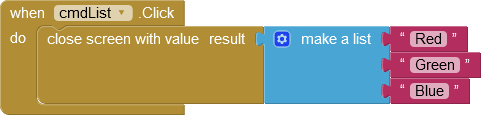
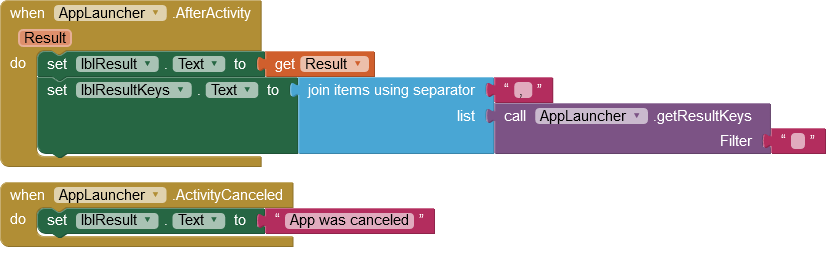
If the called app was terminated regularly, the AfterActivity event is triggered and data can be returned. Like the start values, these are stored internally as key-value pairs in an intent. AI2 apps can provide return values via the blocks close screen with value and close screen with plain text. AI2 sets this value as a key-value pair with the key "APP_INVENTOR_RESULT" in the Intent.
The calling app can evaluate the returned Intent. The extension provides appropriate methods.
- The AfterActivity event has the Result parameter . If the launched app returns a value with the key "APP_INVENTOR_RESULT",the value is converted into a string and made available via the parameter Result.
- The getResultKeys method provides a list of all key values of all key-value pairs.
- The getResultValue method returns the value associated with the specified key as a String.
- The getResultObject method returns the value associated with the specified key as an object, i.e. with the same data type as it was stored by the launched app.
About Intents
Android uses Intent objects to send orders to the system. An Intent contains all information that is necessary to execute the designated action. The AI2 ActivityStarter, for example, uses Intents internally to start other apps.
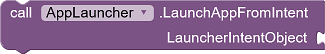
An UrsIntent (Reference) object that is passed to the LaunchAppFromIntent and LaunchForResultFromIntent functions is used to specify which action is to be triggered when the notification is tapped.
This component is a collection of properties. It has neither functions nor events.
The ActionType specifies which action is triggered with the Intent:
- Screen: When the notification is tapped, the designated screen of the app opens.
- Launcher: Tapping the notification will open any app. See also the ActivityStarter documentation at App Inventor.
Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices
Note: Users of Xiaomi devices with Android 10 and newer must grant both permissions!
Android 10
Since Android 10, an app needs additional permissions (SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW) if it wants to start another app while it is running itself in the background (see Restrictions on starting activities from the background, last point). This permission cannot be set by program, but has to be confirmed by the user via a dialog (see Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices).
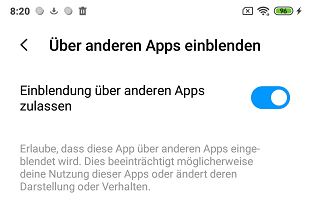
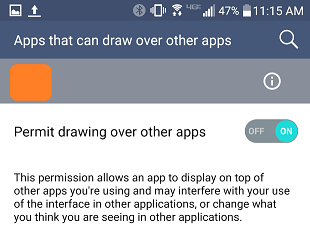
The extension provides the CheckBackgroundLaunchPermission method. The method checks whether the installed Android version has an API level of 29 (Android 10) or higher and whether the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission has been granted. If it is necessary that this permission is granted, a dialog for granting the permission is opened:
 |
 |
|
| German variant | English variant |
The result of the permission request is returned via the AfterBackgroundPermssion event. The new state of the permission is not available immediately after closing the authorization dialog. The event is therefore triggered after a short delay (property PermissionDelay, default 500 ms) after closing the dialog. During this time, the state of the permission is undefined. It is advisable to ensure that no nonsensical data is displayed or problematic entries can be made meanwhile. It is best to put all the concerned screen elements into aVerticalArrangement. This can be temporarily switched invisible or, for example, deactivated via the EnableArrangement method of the UrsAI2ComponentGroup extension ( see example below).
For further detailed handling of this permission you can use:
- Property VersionSDK: Returns the installed API level (29 for Android 10).
- Property CanDrawOverlays: Returns whether the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission is granted.
- Property CanLaunchFromBackground: Returns whether this app when running in the background can start other apps, i.e. either the API level is less than 29 or the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission has been granted.
Xiaomi devices
With Xiaomi devices, regardless of the Android version installed, a additional permission is required if an app wants to start another app while it is itself running in the background. This permission cannot be not set by the program, but has to be confirmed by the user via a dialog (see Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices). The program cannot query whether this permission has already been granted.
The following elements are available to handle this problem:
- Property Manufacturer: Returns the manufacturer name (e.g. "Xiaomi").
- Property IsXiaomi: Returns whether the device comes from the manufacturer Xiaomi.
- Property CurrentLanguage: Returns the set language ("de", "en", etc. see List of ISO 639-1 codes). Helpful for displaying relevant information (see example)
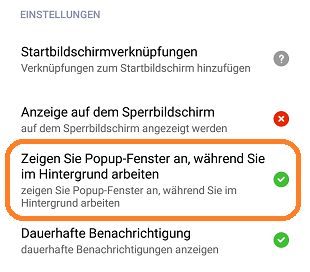
- Method OpenMiuiPermissionEditor: Opens the special Xiaomi permission editor.
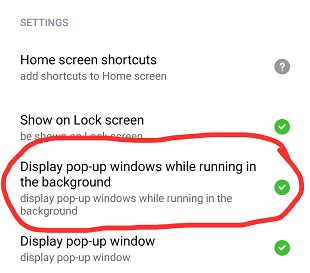
The Xiaomi permission editor:
 |
 |
|
| German variant | English variant |
The sample project shows one way how these permissions can be handled.
You can also get the permision via the Settings app. This blog entry shows how to do it: Enable “display pop-up windows” on new Xiaomi phones. Another access option: Long press the app icon, then select "App-Info".
Reference
| Block | Function | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| App names and package names | ||
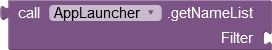 |
Provides the names of the installed and launchable apps as an alphabetically sorted list. A pre-selection can be made using the Filter parameter. Only those apps whose names contain the specified text are returned. Specify an empty text ("") for no filtering. The filter value is not case sensitive. |
Filtering is done with the Java method String.contains(). Before being applied the filter value and the app name are converted to lowercase letters using String.toLowerCase(). |
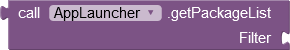 |
Provides the package names of the installed and launchable apps as an alphabetically sorted
list. A pre-selection can be made using the Filter parameter. Only those apps whose names contain the specified text are returned. Specify an empty text ("") for no filtering. The filter value is not case sensitive. |
Filtering is done with the Java method String.contains(). Before being applied the filter value and the app name are converted to lowercase letters using String.toLowerCase(). |
 |
Returns the package name of the app, whose app name was specified in the AppName parameter. | An empty text ("") is returned if no package name could be determined. |
  |
Provides the name of the current app or its package name. | |
| Launching Apps | ||
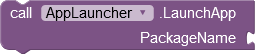 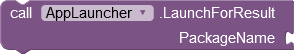 |
Launches the app with the specified package name either as an independent or as a dependent process (see above). | The success of this action will be presented via the AfterAppLaunched event (see below). |
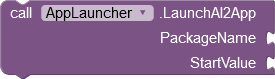 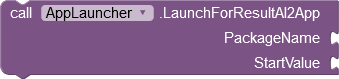 |
Launches the app with the specified package name
either as an independent or as a dependent process. Information to the launched app can be transmitted via the Key/Value parameter pair. Key and Value expect a text as argument. |
If parameters with another type as text (String) are
supplied, AI2 converts them into text. AI2 evaluates the "APP_INVENTOR_START" key and provides the associated value via the getStartValue  method or.
getPlainStartText method or.
getPlainStartText
 method.
method.getStartValue transfers any object type. You can use a List to transfer more than one value. |
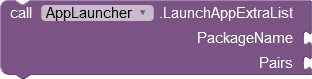  |
Launches the app with the specified package name
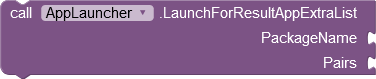
either as an independent or as a dependent process. The Pairs parameter is a list of lists with two values each. The first value is interpreted as a key, the second as an associated value. |
Further informations at http://ai2.appinventor.mit.edu/eference/other/activitystarter.html or https://appinventor.mit.edu/explore/ai2/activity-starter.html |
  |
The LauncherIntentObject specifies which activity is started and the launch options. | See Reference UrsIntent |
 |
Returns the result of the start attempt: 0: successful 1: package not found 2: Pairs not constructed correctly |
|
| Return Values | ||
  |
Specifies the return values. | AI2 transfers the specified values as a key/value pair with the key "APP_INVENTOR_RESULT". |
 |
The launched app has been canceled. | Return values are not available. |
 |
The called app was terminated regularly. Result: Return value of an AI2 app. |
If the launched app returns a key/value pair with the key "APP_INVENTOR_RESULT", the value is converted into a String and presented via the parameter Result . |
 |
Returns a list of all keys of all key/value pairs contained in the returned Intent. | The return value of the method is a List of String. |
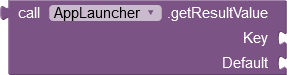 |
Returns the value associated with Key as a String. | The value is converted into a String by the Java function toString. |
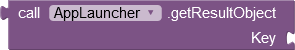 |
Returns the value associated with Key as a Object. | There is no conversion. AI2 passes values as a JSON strings. |
| Other elements | ||
Properties
- CanDrawOverlays
- Returns whether permission SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW is granted.
- CanLaunchFromBackground
- Returns whether you are permitted to lauch apps while in background.
- CurrentLanguage
- Returns the current language, e.g. 'de' or 'en'." (see List of ISO 639-1 codes).
- IsXiaomi
- Returns whether this is a Xiaomi device.
- Manufacturer
- Returns the manufacturer name of the device.
- PermissionDelay
- Delay for internal request of CanLaunchFromBackground after permission dialog was closed (see Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices). The default is 500 ms.
- Version
- Returns the extension's version name.
- VersionSDK
- Returns running Android SDK version (API level).
Methods
- CheckBackgroundLaunchPermission ()
- Checks if lauching apps from the background is permitted and if not, asks for the permission.
- OpenMiuiPermissionEditor ()
- Opens the MIUI permission editor.
Events
- AfterBackgroundPermssion (Result)
- Returns the result of CheckBackgroundLaunchPermission. There is a delay of PermissionDelay milliseconds after the permission dialog is closed (see Additional permissions since Android 10 and on Xiaomi devices).
Reference LauncherIntent
Note:
Since Android 10, the FlagNewTask property must be set to true.
The ActionType specifies which action is triggered with the Intent:
- Screen: When the notification is tapped, the designated screen of the app opens.
- Launcher: Tapping the notification will open any app. See also the ActivityStarter documentation at App Inventor.
The column S marks fields that are relevant for the ActionType Screen, the column L those for the ActionType Launcher.
| Name | Type | S | L | Functionality | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ActionType | choice (Designer only) |
X | X | Specifies the type of action. Possible values are None, Screen, Launcher, Event or GoBack. Different fields are evaluated depending on the ActionType. | None |
| ActivityAction | text | - | X | Specifies the action that will be used to start the Activity. | -none- |
| ActivityClass | text | - | X | Specifies the class part of the specific component that will be started. ActivityPackage and ActivityClass define the Activity to be started when the notification is tapped. |
-none- |
| ActivityPackage | text | - | X | Specifies the class part of the specific component that will be started. ActivityPackage and ActivityClass define the Activity to be started when the notification is tapped. |
-none- |
| DataType | text | - | X | Specifies the MIME type to pass to the Activity. | -none- |
| DataUri | text | - | X | Specifies the data URI that will be used to start the activity. | -none- |
| FlagClearTask | boolean | X | X | This flag will cause any existing task that would be associated with the activity to be cleared before the activity is started. | false |
| FlagClearTop | boolean | X | X | If set, and the Activity being launched is already running in the current Task, then instead of launching a new instance of that Activity, all of the other activities on top of it will be closed and this Intent will be delivered to the (now on top) old Activity as a new Intent. | false |
| FlagExcludeFromRecent | boolean | X | X | If set, the new Activity is not kept in the list of recently launched activities. | false |
| FlagNewTask | boolean | X | X | If set, this
Activity
will become the start of a new
Task on this history stack. Since Android 10 this flag must be set to true. |
true |
| FlagNoAnimation | boolean | X | X | This flag will prevent the system from applying an Activity transition animation to go to the next activity state. | false |
| FlagNoHistory | boolean | X | X | If set, the new Activity is not kept in the history stack. As soon as the user navigates away from it, the activity is finished. | false |
| FlagPreviousIsTop | boolean | X | X | If set and this Intent is being used to launch a new Activity from an existing one, the current Activity will not be counted as the top Activity for deciding whether the new Intent should be delivered to the top instead of starting a new one. The previous Activity will be used as the top, with the assumption being that the current Activity will finish itself immediately | false |
| FlagReorderToFront | boolean | X | X | This flag will cause the launched Activity to be brought to the front of its task's history stack if it is already running. | false |
| FlagResetTaskIfNeeded | boolean | X | X | If set, and this Activity is either being started in a new Task or bringing to the top an existing Task, then it will be launched as the front door of the Task. This will result in the application of any affinities needed to have that Task in the proper state (either moving activities to or from it), or simply resetting that task to its initial state if needed. | false |
| FlagSingleTop | boolean | X | X | If set, the Activity will not be launched if it is already running at the top of the history stack. | false |
| FlagTaskOnHome | boolean | X | X | This flag will cause a newly launching task to be placed on top of the current home activity task (if there is one). That is, pressing back from the task will always return the user to home even if that was not the last activity they saw. This can only be used in conjunction with FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK. | false |
| ScreenStartValue | text | X | - | The start value to be transferred to the Screen to be
opened. Available via Control.getStartValue
|
-none- |
| ScreenToOpen | text | X | - | The name of the Screen to open when you tap the notification. The name of the Screen to open when you tap the notification. | "Screen1" |
Example
The download archive contains two sample apps:
-
 UrsAI2AppLauncherTest.aia: Used to launch other apps..
UrsAI2AppLauncherTest.aia: Used to launch other apps.. -
 UrsAI2AppLauncherTestResponder.aia: Displays start and return values.
UrsAI2AppLauncherTestResponder.aia: Displays start and return values.
Data exchange between two AI2 apps
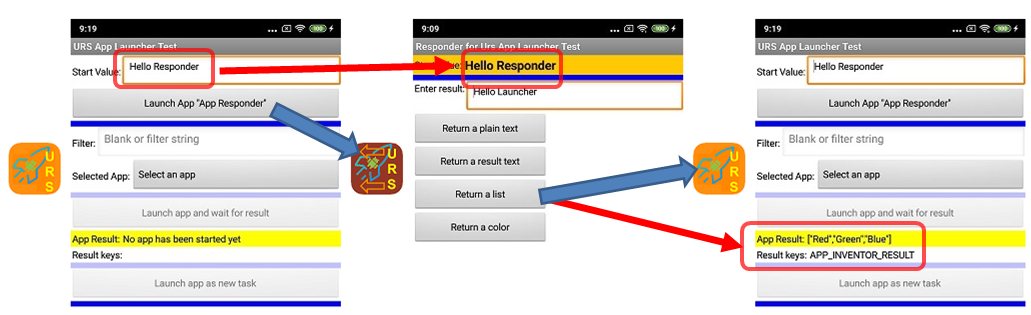
The first example shows the data exchange between two AI2 apps.
Launching via an app list
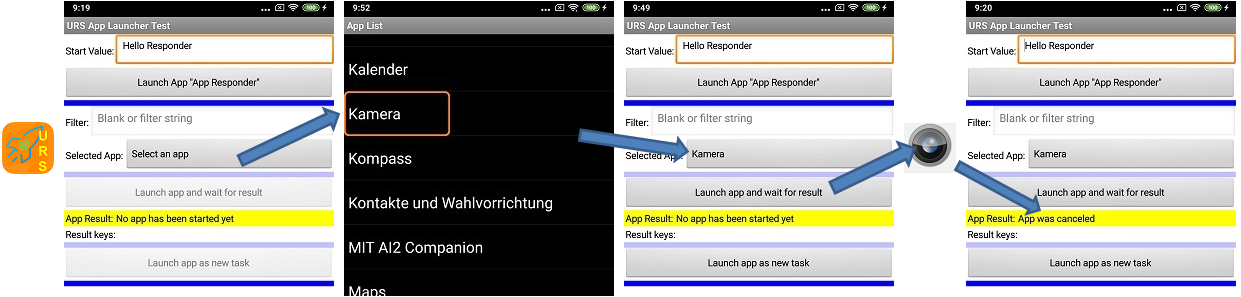
The following example shows how to use the getNameList and PackageFromName methods to launch an app. The call of LaunchForResult results in the starting app being paused until the launched app has terminated.
 |
|||||
| Displays the list of available apps | Choosing the "Kamera" app (It's a German Android version) | Launch the app | Displays termination state of the launched app | ||
Android 10 permissions
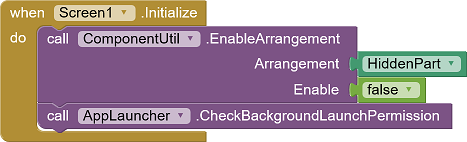
When the app is started (Screen.Initialize), a check is done to see whether other apps can be started from the background. All relevant screen elements are embedded in the HiddenPart VerticalArrangement so that no input is possible in the time between the request for the necessary permission and the response. This arrangement is blocked when the app starts with the EnableArrangement method of my extension UrsAI2ComponentGroup.
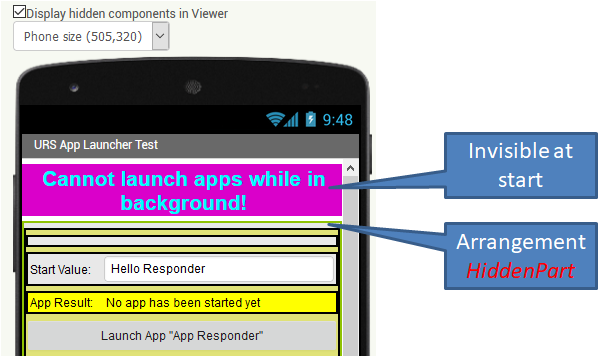 |
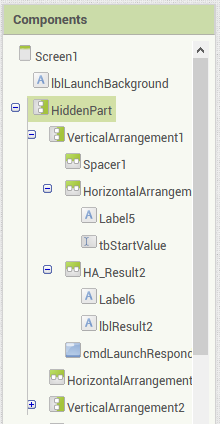 |
|
|||
| There is an invisible warning at the top. All essential elements are embedded in HiddenPart. | All essential elements are embedded in HiddenPart. | When the app starts, HiddenPart is blocked and authorization is checked. |
When the response to the permission request is received, HiddenPart is activated. If the permission to start apps from the background has not been granted, the warning is made visible.
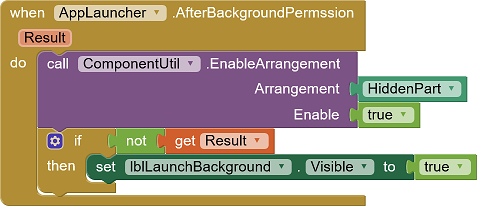
Permissions for Xiaomi devices
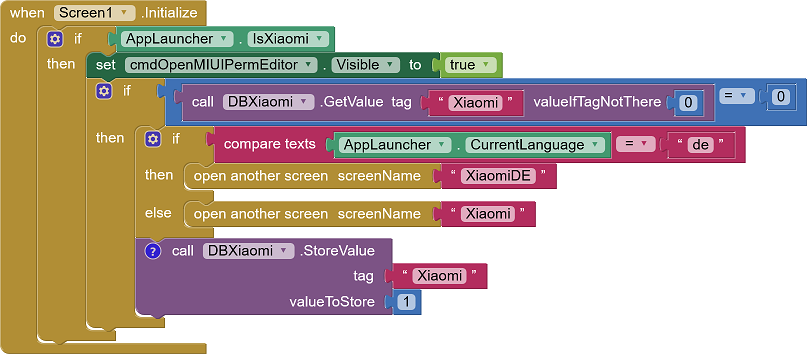
When the app starts, it is checked whether it is a Xiaomi device. In this case, the button to open the Miui permission editor is activated. When the app is started for the first time, a notification screen is shown that asks the user to set the needed permissions. So that this does not happen every time the app is started, a database (TinyDB) stores whether the message has already been displayed. The notification is available in two languages, German and English.
The notification:
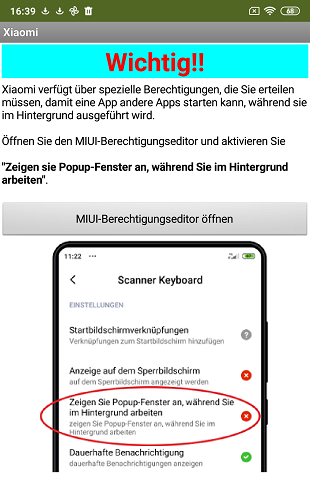 |
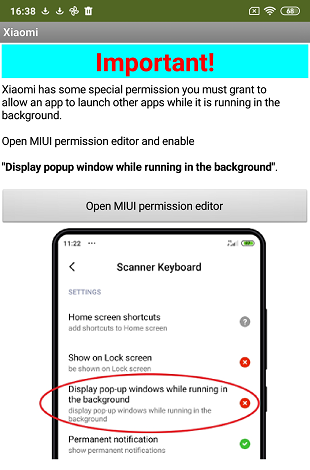 |
|
| German variant | English variant |