| Version | Anpassungen |
|---|---|
| 1.0 (2020-02-29 | Initial version |
| 2.0 (2020-08-18) | - Renamed to UrsAI2Util - Method MoveTaskToBackground added - Method SimulateHomeKey added - Event OnDestroy removed, raising of events in Form.onDestroy is not supported |
| 2.1 (2020-10-27) | Method FileListFromAssets added. |
| 2.2 (2020-12-31) | Methods GetTextWidth, SetX,
SetY, ScreenWidth,
ScreenHeight added. This allows horizontal scrolling to be implemented using a slider. |
| 2.3 (2023-06-15) | Method SetHypertext added. |
| 2.4 (2023-08-12) | Methods for logging added. |
| 3.0 (2023-12-19 | SetX and SetY methods expect values
in DIP (previously in pixels). All visible components can be moved. Methods getY, getY, SetPadding, GetPaddingLeft, GetPaddingTop, GetPaddingRight, GetPaddingBottom, SetBorder added. Properties ScreenDensity, ScreenWidthDIP, ScreenHeightDIP added. |
| 3.1 (2024-03-24) | FinishAndRemoveTask added |
| 3.2 (2025-06-15) |
Members added: |
| 3.3 (2025-08-15) | Method EnableArrangement added. |
Events onPause, onStop, onResume
Functions for manipulating visible components
Hypertext for Label, Button and CheckBox
Download
The ZIP archive UrsAI2Utils for downloading. The archive contains the source code and the compiled binary and a sample project to upload to the App Inventor.
Events onPause, onStop, onResume
The following graphic shows the life cycle of an Android Activity.

For some applications it can be interesting to know the state of the app. The extension provides events that are triggered when the state changes. Unfortunately, only four of these changes can be accessed via the App Inventor Framework. onCreate is already implemented in the screen component as Initialize. onPause, onStop, onResume are provided by this extension.
| Block | Funktion |
|---|---|
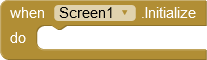 |
The Initialize event is run when the Screen starts and is only run once per screen. |
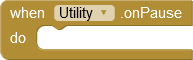 |
The app is (partially) covered. User input is not accepted.1) |
 |
The app is moved to the background. |
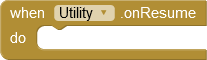 |
The app becomes visible and accepts user input. |
1) In all my attempts at these events, onStop was always triggered after onPause.
StringToHex
This function should make debugging easier. Especially for data exchange purposes it can be interesting to know what the internal representation of a String is. Usually it is UTF-8 coded.
| Block | Funktion |
|---|---|
 |
The string in the argument Text is converted to a string that contains the hexadecimal representation of the individual characters. e.g. "abcß" becomes "61 62 63 C3 9F". |
Image-Import
Byte arrays can be transferred with the MQTT extension, e.g. this may be JPEG images. The method converts the received byte array into a bitmap object and displays it on an App Inventor Image component. This method should not be confused with the Picture property of the component! Picture expects the file path to an image file.
| Block | Funktion |
|---|---|
 |
JPEG: Byte array that contains a JPEG image. ImageBlock: A component of the type Image on which the image is to be displayed. Rotation: Rotation angle. |
A typical use of the block could look like this:
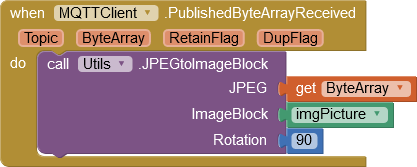
Functions for manipulating visible components
Hypertext for Label, Button and CheckBox
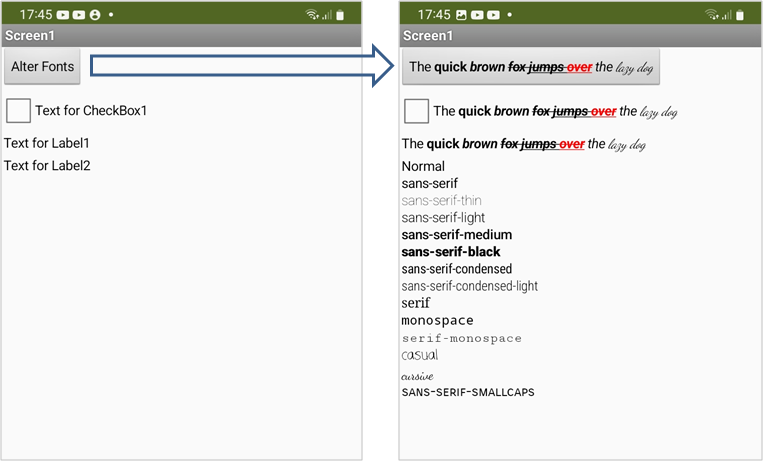
The text formatting options in App Inventor always refer to the entire component. For example, highlighting a single word is not possible in the standard.
The SetHypertext method allows text to be provided with HTML tags and thus to design the text individually. Which HTML tags can be used varies depending on the implementation of the Android system. There are hints at Mark Murphy's Technical Stuff or Daniel Lew's Coding Thoughts. The following example shows the usage:
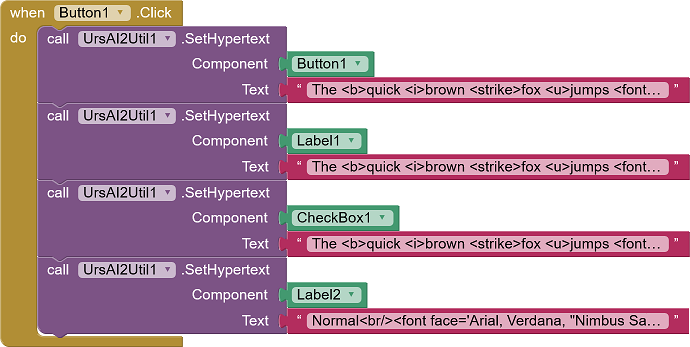
The entries for Button1, Label1 und CheckBox1 for
"The <b>quick <i>brown <strike>fox <u>jumps <font
color="red">over</font></u></strike><i></b> the <font face='cursive'>lazy dog</font>"
and for Label2
"Normal<br/>
<font
face='sans-serif'>sans-serif</font><br/>
<font face='sans-serif-thin'>sans-serif-thin</font><br/>
<font
face='sans-serif-light'>sans-serif-light</font><br/>
<font
face='sans-serif-medium'>sans-serif-medium</font><br/>
<font
face='sans-serif-black'>sans-serif-black</font><br/>
<font
face='sans-serif-condensed'>sans-serif-condensed</font><br/>
<font
face='sans-serif-condensed-light'>sans-serif-condensed-light</font><br/>
<font
face='serif'>serif</font><br/>
<font face='monospace'>monospace</font><br/>
<font
face='serif-monospace'>serif-monospace</font><br/>
<font face='casual'>casual</font><br/>
<font
face='cursive'>cursive</font><br/>
<font face='sans-serif-smallcaps'>sans-serif-smallcaps</font>"
Properties
- ScreenDensity
- Gets the conversion factor from DIP to pixels for this device Pixel = DIP * Density.
- ScreenHeight
- Gets the height of the screen in pixels.
- ScreenHeightDIP
- Gets the height of the screen in DIP.
- ScreenWidth
- Gets the width of the screen in pixels.
- ScreenWidthDIP
- Gets the width of the screen in DIP.
Functions
- GetPaddingBottom(Component )
- Returns the bottom padding of this component.
- GetPaddingLeft(Component )
- Returns the left padding of this component.
- GetPaddingRight(Component )
- Returns the right padding of this component.
- GetPaddingTop(Component )
- Returns the top padding of this component.
- GetTextWidth(Component )
- Gets the length of the text in a text box.
- GetX(Component)
- Retrieves the left position of a component. The specification is made in DIP.
- GetY(Component)
- Retrieves the top position of a component. The specification is made in DIP.
- SetBorder (Component , Color, Width, ExtendPadding)
- Ensures that a frame with the width Width (in DIP) in the color Color is drawn around the component. The frame is drawn in the area of the component. This reduces the distance between the content of the component and its edge. If ExtendPadding is set to true, this is compensated for by extending the padding (see SetPadding).
- SetPadding(Component , Left, Top, Right, Bottom)
- Defines the padding of a component. The specifications are made in DIP.
- SetX(Component , X)
- Specifies the left position of a text box or label. X is specified in DIP. X can be negative.
- SetY(Component , Y)
- Specifies the top position of a text box or label. Y is specified in DIP. Y can be negative.
Functions for output to the Android log
The Android Debug Bridge (adb) allows a log to be displayed, e.g. on a connected PC. These functions can be used to write to the Android-Log.
Properties
- LogTag
- Sets the tag for the functions that do not specify the tag explicitly.
Methods
- LogD(Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag LogTag and the message Msg at the DEBUG level.
- LogE(Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag LogTag and the message Msg at the ERROR level.
- LogI(Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag LogTag and the message Msg at the INFO level.
- LogV(Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag LogTag and the message Msg at the VERBOSE level.
- LogW(Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag LogTag and the message Msg at the WARN level.
- WriteLogD(Tag, Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag Tag and the message Msg at the DEBUG level.
- WriteLogE(Tag, Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag Tag and the message Msg at the ERROR level.
- WriteLogI(Tag, Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag Tag and the message Msg at the INFO level.
- WriteLogV(Tag, Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag Tag and the message Msg at the VERBOSE level.
- WriteLogW(Tag, Msg)
- Outputs a text to the log with the tag Tag and the message Msg at the WARN level.
Functions for raising events
Functions
- CallEvent (Component, EventName)
- Triggers the event specified by EventName in the Component component.
- CallParamEvent (Component, EventName, Parameters)
- Triggers the event specified by EventName in the Component component and passes the values specified in Parameters.
- FireDelayedEvent (Tag, DelayMillis)
- Triggers the DelayedEvent event after the specified number of milliseconds. Tag is used for identification.
- FirePostedEvent (Tag)
- Causes the triggering of the PostedEvent event to be added to the message queue. Tag is used for identification.
Events
- DelayedEvent (Tag)
- The event is triggered by calling the FireDelayedEvent function. Tag is used for identification.
- PostedEvent (Tag)
- The event is triggered by calling the FirePostedEvent function. Tag is used for identification.
Other functions
| Block | Funktion |
|---|---|
 |
Moves the app to the background. |
 |
Simulates pressing the home button. |
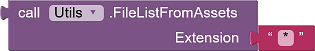 |
Returns a list of the asset file names with the specified extension. "*" return all. |
Properties
- Version
- Gest the version of the extension.
- VersionSDK
- The API level of the currently running Android instance.
Methods
- EnableArrangement (Enable)
- Enables/disables all components registered in the arrangement.
- FileListFromAssets(Extension)
- Returns a list of the asset file names with the specified extension. "*" return all.
- FinishAndRemoveTask ()
- Finishes all activities in this task and removes it from the recent tasks list.
- MoveTaskToBackground()
- Moves the app to the background.
- SimulateHomeKey()
- Simulates pressing the home button.
Events
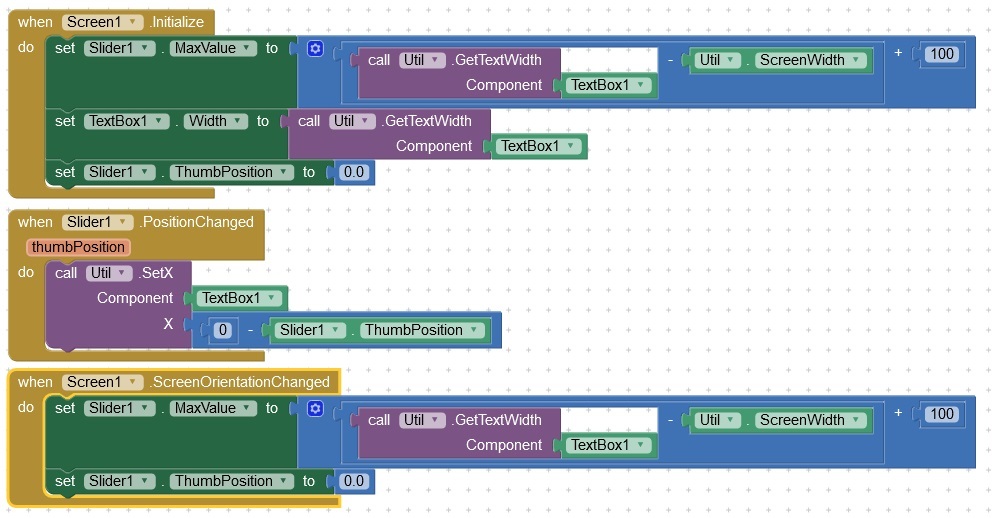
Slider example
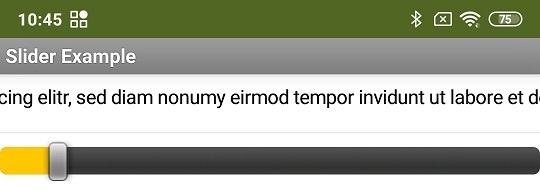
The text in a TextBox is moved horizontally using a slider.
Actually, it just looks like it. The length of the text is determined and the width of the text box is set to this value. The TextBox can now display the entire text and is therefore wider than the embedding container (the screen in the example). The entire TextBox is now moved based on the slider position. The text parts that are outside of the container are then not visible. Overall, it looks as if the text has been moved.
Tools
For developing own extensions I gathered some tips: AI2 FAQ: Develop Extensions.